Clinical Support: Level 1
Build infrastructure for ample vaccine supply and safe distribution
Engage the staff who purchase, distribute, and administer vaccines to determine what vaccines to order and in what amounts. Review patient data, vaccine recommendations, and your organization’s immunization procedures and storage capacity to inform purchasing decisions. Develop protocols for safe handling and distribution to protect patients and staff.
Clinical support for an effective immunization program begins with adequate supplies and up-to-date protocols for safe handling, storage, and distribution. To build this infrastructure, follow the steps below.
Step 1:
Engage staff responsible for vaccine procurement and administration
Consult with relevant stakeholders to inform decision-making around vaccine supply and distribution. These stakeholders typically include:
- Clinic managers
- Lead clinicians who are central points of contact in vaccine administration
- Staff in the purchasing department who are familiar with costs and coding
Also consider engaging relevant leadership such as your Chief Medical Officer, Chief Nursing Officer, and/or Chief Operating Officer.
Step 2:
Determine which supplies to order and how much
Before ordering vaccines, consider:
- Who is getting vaccinated: Compile organizational data for influenza, pneumococcal, Td/Tdap, zoster, RSV, COVID-19, and hepatitis B vaccinations. Look at immunization rates and goals for the upcoming year.
- Where patients are getting vaccinated: Identify vaccination sites, which may include clinics, pharmacies, and other community-based or employer locations. Consider additional factors, such as seasonal and walk-in clinics, drive-through sites, or extended vaccination hours.
- What is forecasted for the year ahead: Adjust orders according to projections, such as the anticipated activity for the flu season.
- How vaccines are being stored: Assess storage capacity to ensure it is sufficient for the order quantity and can accommodate vaccine storage requirements (e.g., temperature control).
Before ordering influenza vaccines, your organization may need to make some key decisions around which products to purchase, such as:
- Single vs. multi-dose vaccines
- Universal vs. population-specific vaccines (e.g., high dose for older adults)
- Mists vs. shots
Examine manufacturer and distributor or wholesaler policies regarding refunds and returning extra stock. If the terms are generous, consider ordering a bit more than initially projected.
Throughout the process, factor in complementary supplies like syringes and safety needles, gloves, bandages, and personal protective equipment for staff involved in vaccine administration.
Step 3:
Protect patients and staff with safe storage and handling practices
Ensure storage and handling protocols are updated on a regular basis and are integrated into clinic workflows as well as staff and provider education. See accompanying tools below to support safe vaccine administration. Some best practices include:
- Assigning a staff person responsibility for monitoring and maintaining temperature control
- Keeping an inventory log with expiration dates
- Rotating stock to ensure older stock is used first (typically new stock is placed behind older stock)
- Ensuring employees’ food and personal items are not stored in same refrigerator as vaccine stock
- Creating a streamlined system for identifying vaccines in storage (e.g., color-coding boxes and vials) to ensure the right vaccine is given in the right dosage every time
- Using safety needles to protect staff from a workplace injury
Vaccine Storage Best Practices
Norton Medical Group
Outlines vaccine storage best practices and provides examples for medication labels, vaccine storage, and storage labeling.
View Tool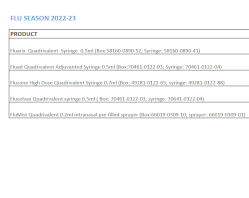
Flu Vaccine Ordering Options
UC San Diego Health
Summarizes an organization’s influenza vaccine order for the 2022-2023 influenza season. Provides information on product, mercury content, latex status, corresponding age group, and cost.
View Tool
Checklist for Safe Vaccine Storage and Handling
Immunize.org
Features a checklist to assist organizations in safeguarding their vaccine supply—from establishing storage and handling procedures to maintaining daily temperature logs. This resource can identify areas of improvement in vaccine management practices.
View Tool
"Supplies You May Need at an Immunization Clinic" Checklist
Immunize.org
Offers a checklist of supplies that may be required at an immunization clinic. Suggested items span a variety of categories including vaccines, clinic documentation, supplies, Vaccine Information Statements, and office materials.
View Tool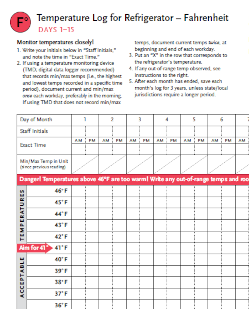
Temperature Log for Refrigerator – Fahrenheit
Immunize.org
Provides a log to monitor Fahrenheit temperature of clinic refrigerators to ensure safe vaccine storage. This log includes a section for documenting any unacceptable storage event with accompanying examples.
View Tool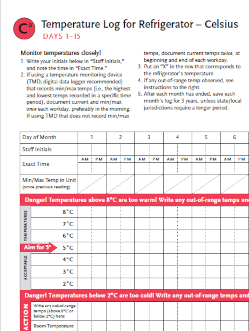
Temperature Log for Refrigerator – Celsius
Immunize.org
Provides a log to monitor Celsius temperature of clinic refrigerators to ensure safe vaccine storage. This log includes a section for documenting any unacceptable storage event with accompanying examples.
View Tool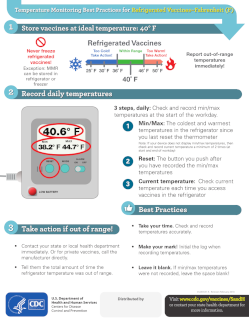
Storage Best Practices for Refrigerated Vaccines - Fahrenheit (F)
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)
Provides action items to follow for safe storing of refrigerated vaccines as well as a knowledge test for staff to identify areas for additional education.
View Tool
Vaccine Storage and Handling Toolkit
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)
Identifies information, recommendations, and resources to assist in properly storing and handling vaccine supply. The comprehensive Toolkit brings together best practices from the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) General Best Practice Guidelines for Immunization, product information from vaccine manufacturers, and results of scientific studies. Of particular note is Section Three, which focuses on vaccine storage and temperature monitoring equipment.
View ToolCampaign Planks
Provider & Staff Education
Clinical Support
IT / Documentation
Patient Education
